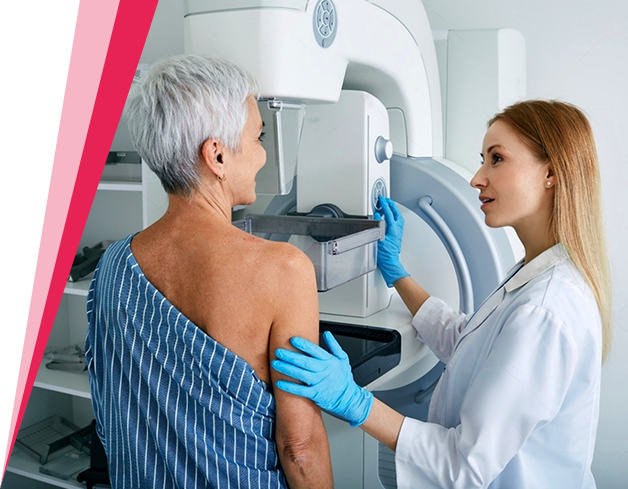
Best Stereotactic Biopsy Doctor in India
Stereotactic VABB
In addition to stereotactic core biopsy, wire and clip placement , VABB is also performed. Tomosynthesis guided procedures have higher precision than Mammographic guided procedures.
What Is It?
Clustered suspicious microcalcifications can be a very early sign of malignancy, particularly typical for ductal carcinoma in situ. Microcalcifications are usually detected on screening mammograms, and most of them cannot be identified on ultrasonography. Lesions detected only on mammography require stereotactic guidance for biopsy, and vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (VABB) is currently the biopsy method of choice for stereotactic biopsies. VABB is considered to be a safe procedure and is comparable to surgical biopsy for the characterization of microcalcifications.
Indication: An impalpable suspicious breast mass or microcalcification poorly visible or not visualized at all on ultrasound but well demonstrated on mammograms is the most common indication for stereotactic biopsy. Even some palpable lesions may benefit from stereotactic biopsy, especially those which are vaguely palpable, small, deep seated, not well demonstrated on ultrasound but better demonstrated on mammograms.
Preparation
- You should not wear deodorant, powder, lotion or perfume under your arms or on your breasts on the day of the exam.
- Prior to a needle biopsy, you should report to your doctor all medications that you are taking (including herbal supplements), and if you have any allergies, recent illnesses or other medical conditions. Your physician may advise you to stop taking aspirin or a blood thinner before your procedure.
- You should be accompany by someone.
- Women should always inform their physician if there is any possibility that they are pregnant because radiation can be harmful to the fetus.
How Is It Done?
It can be done in seated or lying down position. The breast is slightly compressed and held in position throughout the procedure.
- A local anesthetic will be injected into the breast for numbing purposes.
- A very small nick is made in the skin at the site where the biopsy needle is to be inserted. The radiologist then inserts the needle and advances it to the location of the abnormality using the X-ray and computer-generated coordinates. X-ray images are again obtained to confirm that the needle tip is actually within the lesion.
- Tissue samples are then removed using a vacuum-assisted device (VAD); vacuum pressure is used to pull tissue from the breast through the needle into the sampling chamber. Without withdrawing and reinserting the needle, the VAD rotates, positions, and collects additional samples. Typically, eight to ten samples of tissue are collected from around the lesion.
- After this sampling, the needle will be removed and a final set of images will be taken. A small marker may be placed at the site so that it can be located in the future if necessary.
- Once the biopsy is complete, pressure will be applied to stop any bleeding and the opening in the skin is covered with a dressing. No sutures are needed.
- A mammogram will be performed to confirm that the marker is in the proper position.
- This procedure is usually completed within an hour.
Benefits
- The procedure is less invasive than a surgical biopsy, leaves little or no scarring, and can be performed in less than an hour.
- Stereotactic breast biopsy is an excellent way to evaluate calcium deposits or tiny masses that are not visible on ultrasound.
- Stereotactic core needle biopsy is a simple procedure that may be performed on an OPD basis.
- Compared with open surgical biopsy, the procedure is less costly, leaves no scars, and eliminates the risks associated with general anesthesia. These benefits make it a preferable option for many patients.
- Generally, the procedure is not painful and the results are as accurate as when a tissue sample is removed surgically.
- No breast defect remains and, unlike surgery, stereotactic needle biopsy does not distort the breast tissue or make it difficult to read future mammograms.
- The use of a vacuum-assisted device may make it possible to remove the entire lesion.
- Recovery time is brief and patients can soon resume their usual activities.
- No radiation remains in a patient's body after an X-ray examination.
- Within limits the crays have no side effects.
Risks
- Because the vacuum-assisted device removes large pieces of tissue, there is a risk of bleeding and forming a hematoma, or a collection of blood at the biopsy site. The risk, however, appears to be less than one percent of patients.
- An occasional patient has significant discomfort, which can be readily controlled by non-prescription pain medication.
- Any procedure where the skin is penetrated carries a risk of infection. The chance of infection requiring antibiotic treatment appears to be less than one in 1,000.
- Doing a biopsy of tissue located deep within the breast carries a slight risk that the needle will pass through the chest wall, allowing air around the lung that could collapse a lung. This is a rare occurrence.
- There is always a slight chance of cancer from radiation. However, the benefit of an accurate diagnosis far outweighs the risk.
- Women should always inform their physician or X-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant.
Dr. Jyoti Arora is one of the best stereotactic biopsy doctors in South Delhi. As a skilled radiologist, she specializes in Stereotactic Biopsy and Stereotactic VABB (Vacuum-Assisted Breast Biopsy), providing minimally invasive procedures for accurate diagnosis of breast lesions.